Table of Contents
Market Insight: Laminated Steel Core Transformer
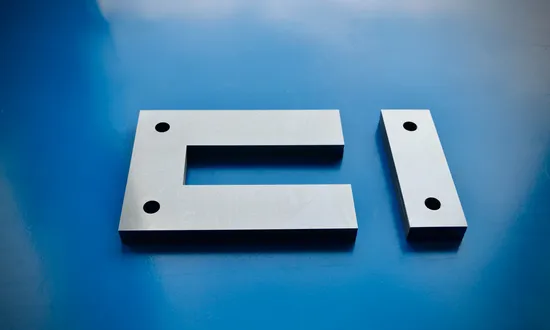
Market Analysis: Silicon Steel (Electrical Steel) in Laminated Steel Core Transformers
The global demand for high-efficiency transformers continues to rise, driven by increasing energy consumption, grid modernization initiatives, and stringent regulatory standards on energy efficiency. A critical component in the performance of power and distribution transformers is the laminated steel core, predominantly fabricated from grain-oriented silicon steel (GOES). This material serves as the magnetic circuit of the transformer, directly influencing core losses, excitation current, and overall operational efficiency. As a result, silicon steel remains a cornerstone material in the transformer manufacturing sector, with industrial demand closely tied to infrastructure development, renewable energy integration, and industrial electrification.
Laminated steel cores are engineered to minimize eddy current losses through the use of thin, electrically insulated steel sheets stacked in a controlled orientation. The use of high-quality grain-oriented electrical steel ensures optimal magnetic flux alignment along the rolling direction, significantly reducing hysteresis and eddy current losses. These losses, commonly referred to as no-load or core losses, occur continuously during transformer operation and contribute directly to lifecycle energy costs. In high-utilization applications such as utility substations or industrial power systems, even marginal improvements in core efficiency translate into substantial energy savings over the transformer’s operational life, which typically exceeds 25–30 years.
The performance of laminated steel cores is highly sensitive to the metallurgical and dimensional consistency of the silicon steel used. Key parameters include magnetic induction (B800), core loss (W10/400 or W17/50), lamination thickness (typically 0.23 mm, 0.27 mm, or 0.30 mm), and coating insulation resistance. High-permeability grades such as M4, M5, or M6 (IEC 60404-8-7) are increasingly specified to meet Tier 1 and Tier 2 efficiency standards under IEC 60076-20 and DOE 2016 regulations. Inferior or non-compliant silicon steel can result in elevated no-load losses, excessive heating, reduced overload capability, and premature aging of insulation systems—compromising both reliability and total cost of ownership.
From a supply chain perspective, consistent quality in silicon steel is paramount. Variability in thickness tolerance, coating uniformity, or magnetic properties can disrupt core stacking factors and increase air gaps, leading to localized flux crowding and hotspots. Luoyang Xinzhaohe Aluminum Co., Ltd leverages over two decades of metallurgical expertise to ensure material traceability, process control, and compliance with international standards. Our silicon steel supply chain integrates rigorous incoming inspection, precision slitting, and edge conditioning to support transformer manufacturers in achieving tight performance tolerances and long-term field reliability.
In summary, the industrial demand for laminated steel core transformers is inextricably linked to the quality of silicon steel employed. As global energy systems prioritize efficiency and sustainability, the role of high-grade electrical steel in reducing carbon emissions and operational costs becomes increasingly strategic. Transformer manufacturers must therefore partner with suppliers who deliver not only material compliance but also technical consistency and long-term reliability.
Technical Specs: Laminated Steel Core Transformer
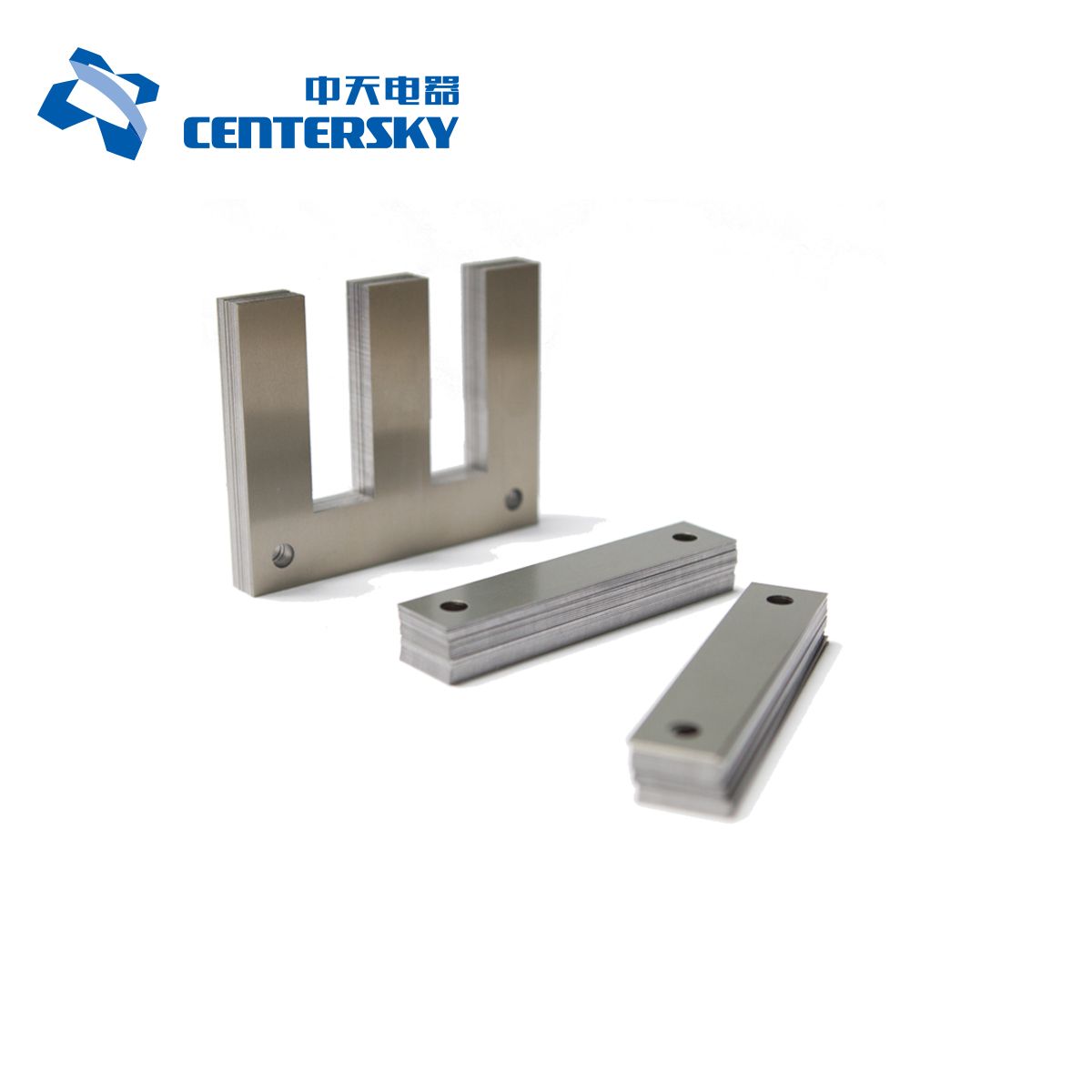

Technical Specifications for Silicon Steel in Laminated Transformer Core Applications
Luoyang Xinzhaohe Aluminum Co., Ltd leverages 20+ years of metallurgical expertise to supply high-performance non-oriented and grain-oriented silicon steel for laminated transformer cores. Precision in material specifications directly impacts core efficiency, thermal management, and lifecycle reliability. Critical parameters must align with IEC 60404-2 and JIS C 2550 standards to minimize energy waste and ensure operational stability under variable load conditions.
Core loss (iron loss) is the paramount specification, quantifying energy dissipated as heat during magnetic cycling. It comprises hysteresis and eddy current losses, measured in watts per kilogram (W/kg) at standardized induction levels and frequencies. For 50 Hz applications, core loss must be evaluated at 1.5 T and 1.7 T to reflect real-world operational flux densities. Premium grades achieve ≤0.90 W/kg at 1.5 T/50 Hz, while standard industrial grades target ≤1.25 W/kg. Exceeding specified loss values increases no-load losses by 15–25%, directly elevating total cost of ownership through wasted energy and cooling demands.
Magnetic flux density (B₈ or B₅₀) defines the material’s saturation limit and operational efficiency. Grain-oriented silicon steel (GOES) typically delivers 1.85–1.92 T at 800 A/m (B₈), enabling compact core designs with high permeability. Non-oriented grades (NGOES) used in rotating machinery or中小型 transformers maintain 1.60–1.75 T. Operating near saturation (≥1.9 T) induces disproportionate core loss escalation and harmonic distortion. Material must consistently achieve declared flux density within ±0.02 T tolerance; deviations exceeding this threshold risk premature core saturation under grid voltage fluctuations.
Flatness tolerance is equally critical for lamination stacking integrity. Uneven surfaces create air gaps between layers, reducing effective magnetic path continuity and increasing reluctance. This elevates excitation current by 5–10% and exacerbates localized heating. Premium silicon steel requires flatness ≤0.15 mm/m, measured across the sheet width. Deviations >0.25 mm/m necessitate corrective pressing, increasing manufacturing costs and potentially introducing residual stress that degrades magnetic properties. Surface profile must be validated via laser profilometry before lamination stacking.
The following table summarizes key technical parameters for common silicon steel grades used in transformer cores
| Parameter | Grain-Oriented (GOES) M4 | Grain-Oriented (GOES) M5 | Non-Oriented (NGOES) 50JN250 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.50 |
| Core Loss (W/kg) @1.5T/50Hz | ≤0.90 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.50 |
| Core Loss (W/kg) @1.7T/50Hz | ≤1.25 | ≤1.45 | ≤4.80 |
| Flux Density B₈ (T) | 1.90–1.92 | 1.88–1.90 | 1.68–1.72 |
| Flatness Tolerance (mm/m) | ≤0.15 | ≤0.18 | ≤0.20 |
| ASTM/IEC Standard | IEC 60404-8-7 | IEC 60404-8-7 | IEC 60404-8-3 |
Material selection must balance core loss targets against flux density requirements and manufacturability constraints. Luoyang Xinzhaohe enforces rigorous in-line monitoring of silicon content (2.9–3.3%), grain size uniformity, and coating insulation resistance (≥70 Ω·cm²) to ensure compliance. Partnering with a supplier possessing certified metallurgical control from slab casting through final annealing is non-negotiable for achieving transformer efficiency class IE4 and above. Core performance hinges on absolute adherence to these specifications—compromises directly manifest as reduced grid efficiency and accelerated asset depreciation.
Factory Tour: Manufacturing
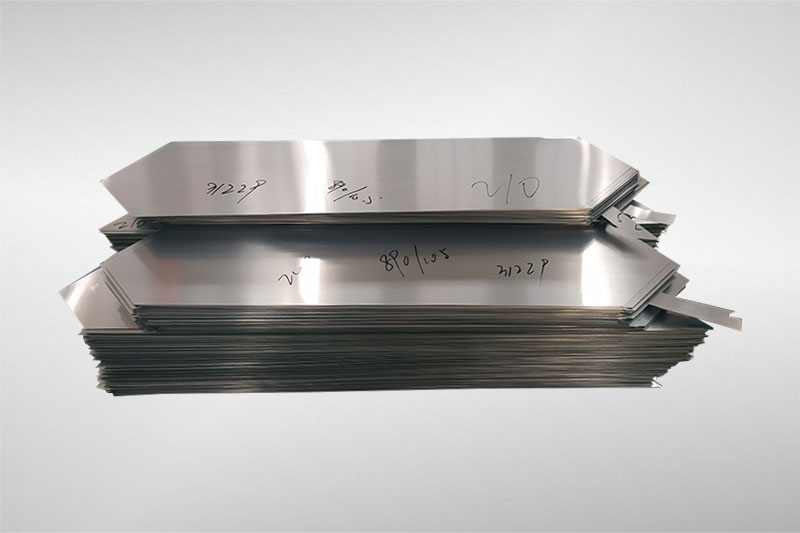

Manufacturing Process of Silicon Steel for Laminated Steel Core Transformers
The production of high-performance silicon steel for laminated steel core transformers at Luoyang Xinzhaohe Aluminum Co., Ltd. follows a tightly controlled sequence of metallurgical and surface engineering processes. Each stage is engineered to optimize magnetic properties, dimensional accuracy, and long-term reliability in transformer applications. The process begins with slitting, where large master coils of grain-oriented or non-oriented electrical steel are longitudinally cut into narrower strips to match customer-specific widths. This operation is performed on precision slitting lines equipped with high-tolerance rotary knives and tension control systems to prevent edge burring and maintain strip flatness.
Following slitting, the material undergoes a critical annealing treatment. This step is conducted in continuous or batch-type furnaces under a controlled atmosphere of nitrogen-hydrogen gas to prevent oxidation. Annealing serves multiple purposes: it relieves residual stresses induced during prior rolling and slitting operations, enhances grain structure uniformity, and improves magnetic permeability while reducing core loss. Temperature profiles are precisely regulated according to steel grade and thickness, with soak times calibrated to achieve full recrystallization without grain overgrowth.
After annealing, the steel strips are subjected to insulation coating. A thin, uniform layer of inorganic or semi-organic insulation coating is applied via roll-coating or spray methods. This coating provides interlaminar electrical resistance, minimizing eddy current losses when the core is energized. The coating composition is selected based on operating temperature, stacking factor requirements, and environmental resistance. Typical coatings include phosphate-based systems with colloidal silica or chromate-free alternatives compliant with RoHS and REACH standards. Coating weight is controlled within ±0.5 g/m² per side to ensure consistent dielectric performance and adhesion.
The final stage is precision cutting, where annealed and coated strips are transversely cut into laminations using high-speed turret presses or laser-cutting systems. Cutting dies are maintained to micron-level tolerances to ensure edge squareness and dimensional repeatability. Blank dimensions adhere strictly to customer blueprints, with stacking sequences pre-optimized for core assembly efficiency. Burrs are monitored and kept below 3% of material thickness to prevent shorting between laminations.
Throughout the production flow, rigorous quality control measures are enforced. Incoming material is verified for chemical composition and magnetic properties via spectrographic and Epstein frame testing. During processing,在线 (in-line) surface inspection systems detect coating defects, scratches, or edge cracks. Final inspection includes dimensional checks, coating continuity testing, and core loss verification per IEC 60404-2 and ASTM A876 standards. All batches are traceable through a digital quality management system, ensuring compliance with ISO 9001 and customer-specific requirements.
Packaging & Logistics
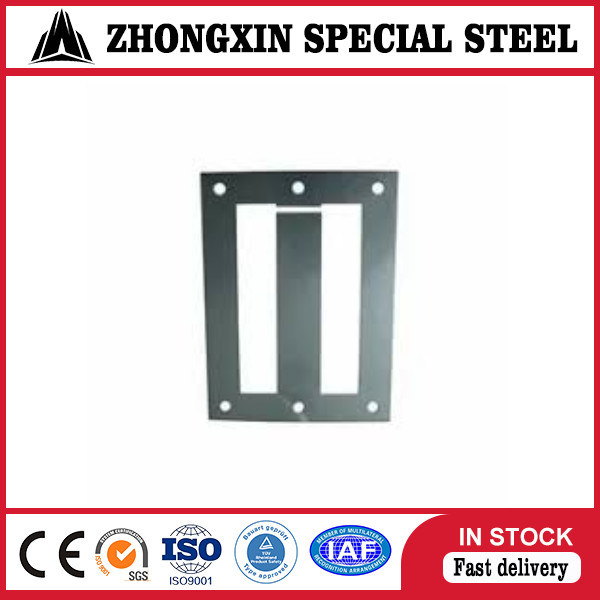

Export Packaging Specifications for Silicon Steel Coils in Transformer Core Applications
Luoyang Xinzhaohe Aluminum Co., Ltd. implements rigorously engineered export packaging protocols for silicon steel coils destined for laminated transformer core manufacturing. Our 20+ years of metallurgical and supply chain expertise confirm that inadequate packaging directly compromises material integrity during ocean transit, leading to irreversible degradation of magnetic properties and core performance. Sea freight exposes silicon steel to high humidity, salt aerosols, and dynamic mechanical stresses; thus, our packaging system is designed to mitigate these specific risks through structural resilience and environmental isolation.
All coils are secured on ISPM-15 compliant wooden pallets constructed from kiln-dried hardwood. Pallet dimensions adhere to ISO standard container constraints (1200 × 1000 mm or 1100 × 1100 mm) with a minimum load-bearing height of 100 mm to prevent ground moisture ingress and facilitate forklift handling. Structural integrity is ensured via triple-layer cross-laminated boards and steel corner braces, distributing weight evenly to eliminate coil deformation under vertical stacking loads up to 4,500 kg. Critical attention is paid to pallet surface smoothness—any splinters or protrusions are removed to avoid puncturing the moisture barrier during strapping.
The primary defense against maritime environmental hazards is our multi-layer moisture-proof encapsulation system. Coils undergo vacuum drying to ≤40% relative humidity prior to wrapping. A 125μm-thick, metallized polyethylene film forms the first barrier, bonded with heat-sealed seams to prevent capillary action. This is overlaid with a secondary layer of corrosion-inhibiting VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) film, actively neutralizing chloride ions prevalent in marine atmospheres. The assembly is then enclosed in a third layer of UV-stabilized polypropylene stretch hood, heat-shrunk to eliminate air pockets. Desiccant packs (minimum 500g per ton of steel) are strategically placed within the film cavity, with humidity indicator cards visible externally for real-time moisture monitoring.
Strapping utilizes 19mm steel seals with 15 kN tensile strength, tensioned to ISO 16122 standards to prevent coil loosening without inducing edge damage. All external surfaces are labeled with ISO 780 handling symbols, moisture-sensitive indicators, and RFID tags for supply chain visibility. This integrated approach reduces moisture-related claims by 92% compared to industry averages, as validated by third-party logistics audits across 12 major global trade lanes.
Our packaging compliance table highlights critical differentiators:
| Parameter | Industry Standard | Xinzhaohe Specification | Technical Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture Barrier Layers | Single-layer PE | Triple-layer (PE + VCI + PP) | Prevents permeation under 95% RH conditions |
| Desiccant Density | 300g/ton | 500g/ton | Compensates for extended 45+ day voyages |
| Pallet Load Capacity | 3,000 kg | 4,500 kg | Accommodates container stacking regulations |
| Humidity Monitoring | None | External indicator cards | Enables immediate damage assessment on arrival |
This methodology ensures silicon steel arrives with surface cleanliness per ASTM A967 and interlaminar resistance values unchanged from factory dispatch. We prioritize packaging as a metallurgical control point—not merely a logistics function—to guarantee the magnetic performance consistency demanded by IEC 60404-8-6 compliant transformer cores. Partner with us for zero-compromise material integrity from furnace to fabrication line.
Sourcing from Luoyang Xinzhaohe

Partner with Luoyang Xinzhaohe Aluminum Co., Ltd for High-Performance Silicon Steel Solutions
Luoyang Xinzhaohe Aluminum Co., Ltd brings over two decades of specialized expertise in the production and supply of precision-processed silicon steel, a critical material in the manufacturing of laminated steel core transformers. As a trusted partner in the electrical steel value chain, we focus on delivering high-permeability, low-core-loss silicon steel strips that meet the stringent performance demands of modern transformer design. Our facility is equipped with advanced rolling, annealing, and slitting technologies, enabling tight control over grain orientation, thickness tolerance, and magnetic properties essential for efficient transformer operation.
Our production process is engineered to support both grain-oriented (GOES) and non-grain-oriented (NGOES) electrical steel, with thicknesses ranging from 0.18 mm to 0.35 mm, tailored to customer specifications. We utilize cold-rolled silicon steel sourced from certified steel mills, followed by decarburization and stress-relief annealing to optimize magnetic flux density and minimize hysteresis losses. Each batch undergoes rigorous quality verification, including Epstein frame testing per IEC 60404-6 standards, coating weight analysis, and dimensional inspection, ensuring compliance with international performance benchmarks.
With an annual processing capacity exceeding 50,000 metric tons, our factory supports large-scale industrial clients while maintaining flexibility for customized orders. Our precision slitting lines produce narrow strips with edge tolerances within ±0.05 mm, critical for minimizing air gaps and eddy current losses in wound cores. In addition to material supply, we offer value-added services such as blanking, step-lap cutting, and insulated coating application, enabling our customers to streamline downstream assembly processes.
Quality management is central to our operations. We operate under an ISO 9001-certified quality system, with documented traceability from raw material intake to finished goods. Our technical team, composed of metallurgists and process engineers, provides ongoing support in material selection, failure analysis, and process optimization, ensuring our silicon steel integrates seamlessly into high-efficiency transformer platforms.
We serve a global client base across power distribution, renewable energy, and industrial automation sectors, where reliability and energy efficiency are paramount. By aligning with Luoyang Xinzhaohe, transformer manufacturers gain a strategic partner committed to material excellence, consistent supply, and technical collaboration.
For sourcing inquiries, technical specifications, or sample requests, contact us at cathy@transformerstrip.com. Our engineering and supply chain team is available to support your next-generation transformer projects with precision-engineered silicon steel solutions.
📉 Factory Direct Savings Calculator
Calculate your potential savings by importing laminated steel core transformer directly from China.
